What Is the Respiratory System?
Respiratory System Problems :The respiratory system is a group of organs and tissues that work together to help you breathe. Its main job is to move oxygen into your bloodstream and remove carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism.
This process, called gas exchange, takes place in the lungs—but it involves much more than just the lungs.
Key Parts of the Respiratory System
Here’s a quick overview of Respiratory System Problems its major components:
- Nose and Nasal Cavity: Air enters through the nose, where it’s filtered, warmed, and humidified.
- Pharynx and Larynx: The pharynx (throat) is a passageway for both air and food. The larynx (voice box) routes air into the correct pathway and helps you speak.
- Trachea: Commonly known as the windpipe, the trachea carries air to the lungs.
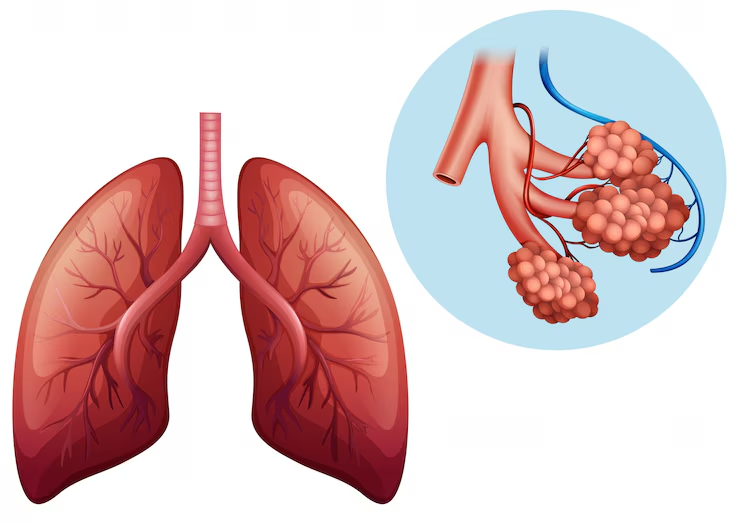
- Bronchi and Bronchioles: The trachea splits into two bronchi, one for each lung. These branch into smaller bronchioles that spread throughout the lungs.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs at the ends of bronchioles where gas exchange occurs. They’re surrounded by capillaries that absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
How Breathing Works
Breathing is an automatic process, controlled by the brainstem. Here’s how it happens:
- Inhalation: Your diaphragm contracts and moves downward, creating space in your chest. This negative pressure draws air into your lungs.
- Gas Exchange: Oxygen from the air passes into your blood in the alveoli, while carbon dioxide moves from your blood into the alveoli.
- Exhalation: Your diaphragm relaxes, pushing air (now rich in carbon dioxide) out of your lungs.
Why Is the Respiratory System Important?
Respiratory System Problems :Oxygen fuels every cell in your body. Without it, cells can’t produce energy, and your organs can’t function. Likewise, removing carbon dioxide prevents your blood from becoming too acidic.
Common Respiratory Conditions
Respiratory System Problems :Several health issues can affect the respiratory system, such as:
- Asthma: Airways narrow and swell, making breathing difficult.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A group of lung diseases that block airflow.
- Pneumonia: Infection inflames the alveoli.
- Lung Cancer: Abnormal cell growth in lung tissue.
Protecting your respiratory system through clean air, regular exercise, avoiding smoking, and staying hydrated is vital for overall health.
Final Thoughts
The respiratory system might work silently behind the scenes, but it plays a starring role in your survival and well-being. Understanding how it works can help you appreciate your breath—and take better care of it.
FAQ: Respiratory System Problems
1. What is the respiratory system?
The respiratory system includes the lungs, airways, and muscles involved in breathing. It is responsible for taking in oxygen and removing carbon dioxide from the body.
2. What are common respiratory system problems?
Common issues include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchitis, pneumonia, lung infections, pulmonary fibrosis, and lung cancer.
3. What symptoms indicate a respiratory problem?
Symptoms can include coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness, persistent mucus production, fatigue, and sometimes fever.
4. What causes respiratory problems?
Causes vary by condition but may include infections (viral or bacterial), smoking, exposure to pollutants or allergens, genetic factors, and chronic diseases.
5. How are respiratory problems diagnosed?
Doctors may use physical exams, chest X-rays, CT scans, pulmonary function tests, blood tests, and sometimes sputum analysis or bronchoscopy.
6. Can respiratory problems be prevented?
Prevention includes avoiding smoking, reducing exposure to air pollutants and allergens, practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated (e.g., flu and pneumonia vaccines), and maintaining overall lung health.
7. How are respiratory problems treated?
Treatment depends on the condition but may involve medications (like inhalers, steroids, antibiotics), oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery.
8. When should I see a doctor?
Seek medical attention if you experience severe shortness of breath, chest pain, persistent cough, coughing up blood, or if your symptoms worsen or do not improve with treatment.
9. Can respiratory problems be chronic?
Yes, some respiratory diseases like asthma, COPD, and pulmonary fibrosis are chronic and require ongoing management.
10. Are respiratory problems contagious?
Some respiratory infections, like the common cold, flu, and pneumonia, can be contagious. Chronic conditions like asthma and COPD are not contagious.
